What Are Activities For Concept Application In Learning Cycles
All-time Education Practices
Learning Bicycle
The lesson plans on the AGPA website use the Learning Wheel every bit the instructional model for its lesson plans. The learning bike rests on constructivism as its theoretical foundation. "Constructivism is a dynamic and interactive model of how humans learn" (Bybee, 1997, p. 176). A constructivist perspective assumes students must exist actively involved in their learning and concepts are non transmitted from teacher to student but constructed by the student. In the early on 1960's, Robert Karplus and his colleagues proposed and used an instructional model based on the work of Piaget. This model would eventually be called the Learning Cycle. (Atkin & Karplus, 1962). Numerous studies have shown that the learning cycle as a model of instruction is far superior to transmission models in which students are passive receivers of noesis from their teacher (Bybee, 1997). Equally an instructional model, the learning wheel provides the agile learning experiences recommended by the National Science Instruction Standards (National Research Council, 1996).
The learning cycle used in these lesson plans follows Bybee'south (1997) 5 steps of Appointment, Exploration, Explanation, Elaboration, and Evaluation. As in any cycle, there's really no stop to the process. Subsequently elaboration ends, the engagement of the side by side learning cycle begins. Evaluation is not the concluding stride. Evaluation occurs in all four parts of the learning cycle. The description of each part of the learning cycle draws extensively from Smith's work.
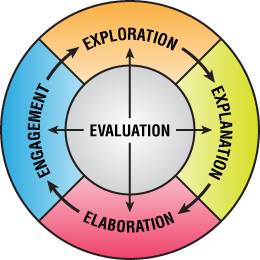
A. Engagement:
Appointment is a time when the teacher is on center stage. The teacher poses the problem, pre-assesses the students, helps students make connections, and informs students well-nigh where they are heading.
The purpose of engagement is to:
- Focus students' attending on the topic.
- Pre-assess what students' prior noesis.
- Inform the students about the lesson'south objective(southward).
- Remind students of what they already know that they volition need to apply to learning the topic at paw.
- Pose a problem for the students to explore in the next phase of the learning wheel.
Evaluation of Engagement: Evaluation's role in engagement revolves around the pre-assessment. Discover out what the students already know virtually the topic at hand. The teacher could ask questions and take the students respond orally and/or in writing.
B. Exploration:
At present the students are at the center of the activeness as they collect data to solve the trouble. The teacher makes sure the students collect and organize their data in order to solve the problem. The students need to be active. The purpose of exploration is to have students collect information that they can utilise to solve the problem that was posed.
Evaluation of Exploration: In this portion of the learning cycle the evaluation should primarily focus on process, i.eastward., on the students' data drove, rather than the product of the students' data collection. Teachers ask themselves questions such as the following:
- How well are the students collecting data?
- Are they carrying out the procedures correctly?
- How do they record the information?
- Is information technology in a logical grade or is it haphazard?
C. Explanation:
In this stage of the process, students use the data they have collected to solve the problem and report what they did and try to figure out the answer to the problem that was presented. The teacher too introduces new vocabulary, phrases or sentences to label what the students have already figured out.
Evaluation of Explanation: Evaluation here focuses on the process the students are using -- how well can students use the data they've collected, plus what they already knew to come upwards with new ideas? Using questions, the teacher can assess the students' comprehension of the new vocabulary and new concepts.
D. Elaboration:
The teacher gives students new information that extends what they accept been learning in the earlier parts of the learning bike. At this stage the instructor also poses problems that students solve by applying what they take learned. The bug include both examples and non-examples.
Evaluation of Elaboration: The evaluation that occurs during elaboration is what teachers usually call back of every bit evaluation. Sometimes teachers equate evaluation with "the exam at the finish of the chapter." When teachers have the students practice the application problems as part of elaboration, these application problems are "the examination."
Additional RESOURCES
Journal Articles - To access most of these Periodical Articles, you must be a student, faculty or staff member at an OhioLINK affiliated institution. Admission to OhioLINK may be available to Ohioans through their local, public, or school libraries. Contact OPLIN, INFOhio, or your local library for more than information.
Understanding the Learning Cycle: Influences on Abilities to Embrace the Arroyo past Pre-service Elementary School Teachers
Science Education, Vol. 84, Issue: 1, Jan 2000. pp. 43 - 50
Settlage, John
The purpose of this report was to deepen scientific discipline teacher educators' knowledge about the process of instilling the learning cycle within the teaching repertoire of unproblematic educational activity majors. A previous written report revealed great variability in preservice teachers' capacity to empathise the learning wheel; the current study was designed to explore factors contributing to this state of affairs. Attitudes toward science and education efficacy were posited to explain the charge per unit at which students...
Students' Science Perceptions and Enrolment Decisions in Differing Learning Cycle Classrooms
Journal of Research in Science Teaching, Vol. 38, Event: 9, November 2001. pp. 1029 - 1062
Cavallo, Ann M.Fifty.; Laubach, Timothy A.
This investigation examined 10th-grade biology students' decisions to enroll in elective scientific discipline courses, and explored certain attitudinal perceptions of students that may be related to such decisions. The pupil science perceptions were focused on student and classroom attitudes in the context of differing learning cycle classrooms (loftier paradigmatic/high inquiry, and depression paradigmatic/low enquiry). The study too examined possible differences in enrollment decisions/intentions and...
Cognition management in pursuit of learning: the Learning with Cognition Bike
Journal of Informatics, Vol. 27, Event: 4, Baronial 2001. pp. 227-237
Rowley, Jennifer
This newspaper suggests that knowledge and learning are closely intertwined. An overview of some of the primal differences between the respective concepts of the learning organisation and knowledge direction forms a footing for exploring the link between these 2 concepts. Both concepts are under development. A model that contributes to the formation of an ontology for analytic discussion, and...
Integrating Concept Mapping and the Learning Cycle to Teach Improvidence and Osmosis Concepts to High School Biological science Students
Science Education, Vol. 85, Issue: half-dozen, November 2001. pp. 615 - 635
Odom, Arthur L.; Kelly, Paul V.
This study explores the effectiveness of concept mapping, the learning bike, expository education, and a combination of concept mapping/learning wheel in promoting conceptual agreement of diffusion and osmosis. Four loftier school biological science classes were taught diffusion and osmosis concepts with the aforementioned treatments. Conceptual understanding was assessed immediately and seven weeks after instruction with the Diffusion and Osmosis Diagnostic Test (DODT). The results indicated the...
Evaluating Online CPD Using Educational Criteria Derived from the Experiential Learning Cycle
British Periodical of Educational Technology, Vol. 33, Issue: 4, September 2002. pp. 367-378
Friedman, Andrew; Watts, David; Croston, Judith; Durkin, Catherine
A set of educational evaluation criteria for online continuing professional development (CPD) courses is developed using Kolb'due south (1984) experiential learning cycle theory. These criteria are used to evaluate five courses provided by online CPD websites. It was plant that these online CPD courses fail parts of the learning cycle. Suggestions for improvements in these areas are given...
The Workplace Learning Cycle: A Problem-based Curriculum Model for the Preparation of Workplace Learning Professionals
Journal of Workplace Learning: Employee Counselling Today, Vol. 16, Issue: 6, 2004. pp. 341-349
O'Connor, Bridget N.
Building on the conceptual foundations suggested in the previous 2 papers in this issue, this commodity describes the application of a workplace learning wheel theory to the construction of a curriculum for a graduate-level course of written report in workplace education. As a manner to set chief learning officers and heads of corporate universities, the piece argues, 1 can appoint students in the procedure of analyzing the learning and knowledge-use in a piece of work environment through the lenses of the...
Websites
http://books.google.com/
This is a 300 page collection of articles relating to the nature of scientific discipline in science teaching and concentrates on diverse rationales and strategies. In the section Communicating the Nature of Science Courses and Class Elements, there is a an article on elementary scientific discipline methods that deals with the learning cycle likewise as other educational activity strategies.
http://eric.ed.gov/
Originally developed in an uncomplicated science program chosen the Science Curriculum Comeback Study, the learning cycle (LC) teaching arroyo involves students in an active learning process modeled on four elements of Jean Piaget's theory of cerebral development: physical experience, referring to the biological growth of the central nervous system; social interaction; physical maturation; and cocky-regulation, the agile process of forming concepts. The LC approach consists of three phases: exploration, concept introduction, and concept application. Implementing the LC requires a shift in educational philosophy from the view of students as empty vessels to exist filled with large amounts of information to the use of strategies emulating scientific methodology and incorporating recent cognitive science findings.
http://eric.ed.gov/
A learning bicycle lesson consists of three phases: concept exploration, concept introduction, and concept application. Describes the application of the learning wheel model to the blueprint of inservice and preservice teacher instruction curriculum.
What Are Activities For Concept Application In Learning Cycles,
Source: https://uakron.edu/polymer/agpa-k12outreach/best-teaching-practices/learning-cycle
Posted by: whitesideitere1944.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are Activities For Concept Application In Learning Cycles"
Post a Comment